Wazawaka Goes Waka Waka
lundi 14 février 2022 à 19:22In January, KrebsOnSecurity examined clues left behind by “Wazawaka,” the hacker handle chosen by a major ransomware criminal in the Russian-speaking cybercrime scene. Wazawaka has since “lost his mind” according to his erstwhile colleagues, creating a Twitter account to drop exploit code for a widely-used virtual private networking (VPN) appliance, and publishing bizarre selfie videos taunting security researchers and journalists.

Wazawaka, a.k.a. Mikhail P. Matveev, a.k.a. “Orange,” a.k.a. “Boriselcin,” showing off his missing ring finger.
In last month’s story, we explored clues that led from Wazawaka’s multitude of monikers, email addresses, and passwords to a 30-something father in Abakan, Russia named Mikhail Pavlovich Matveev. This post concerns itself with the other half of Wazawaka’s identities not mentioned in the first story, such as how Wazawaka also ran the Babuk ransomware affiliate program, and later became “Orange,” the founder of the ransomware-focused Dark Web forum known as “RAMP.”
The same day the initial profile on Wazawaka was published here, someone registered the Twitter account “@fuck_maze,” a possible reference to the now-defunct Maze Ransomware gang.
The background photo for the @fuck_maze profile included a logo that read “Waka Waka;” the bio for the account took a swipe at Dmitry Smilyanets, a researcher and blogger for The Record who was once part of a cybercrime group the Justice Department called the “largest known data breach conspiracy ever prosecuted.”
The @fuck_maze account messaged me a few times on Twitter, but largely stayed silent until Jan. 25, when it tweeted three videos of a man who appeared identical to Matveev’s social media profile on Vkontakte (the Russian version of Facebook). The man seemed to be slurring his words quite a bit, and started by hurling obscenities at Smilyanets, journalist Catalin Cimpanu (also at The Record), and a security researcher from Cisco Talos.
At the beginning of the videos, Matveev holds up his left hand to demonstrate that his ring finger is missing. This he smugly presents as evidence that he is indeed Wazawaka.
The story goes that Wazwaka at one point made a bet wherein he wagered his finger, and upon losing the bet severed it himself. It’s unclear if that is the real story about how Wazawaka lost the ring finger on his left hand; his remaining fingers appear oddly crooked.
“Hello Brian Krebs! You did a really great job actually, really well, fucking great — it’s great that journalism works so well in the US,” Matveev said in the video. “By the way, it is my voice in the background, I just love myself a lot.”
In one of his three videos, Wazawaka says he’s going to release exploit code for a security vulnerability. Later that same day, the @fuck_maze account posted a link to a Pastebin-like site that included working exploit code for a recently patched security hole in SonicWall VPN appliances (CVE-2021-20028).
When KrebsOnSecurity first started researching Wazawaka in 2021, it appeared this individual also used two other important nicknames on the Russian-speaking crime forums. One was Boriselcin, a particularly talkative and brash personality who was simultaneously the public persona of Babuk, a ransomware affiliate program that surfaced on New Year’s Eve 2020.
The other handle that appeared tied to Wazawaka was “Orange,” the founder of the RAMP ransomware forum. I just couldn’t convincingly connect those two identities with Wazawaka using the information available at the time. This post is an attempt to remedy that.
On Aug. 26, 2020, a new user named Biba99 registered on the English language cybercrime forum RaidForums. But the Biba99 account didn’t post to RaidForums until Dec. 31, 2020, when they announced the creation of the Babuk ransomware affiliate program.
On January 1, 2021, a new user “Babuk” registered on the crime forum Verified, using the email address teresacox19963@gmail.com, and the instant message address “admin@babuk.im.” “We run an affiliate program,” Babuk explained in their introductory post on Verified.
A variety of clues suggest Boriselcin was the individual acting as spokesperson for Babuk. Boriselcin talked openly on the forums about working with Babuk, and fought with other members of the ransomware gang about publishing access to data stolen from victim organizations.
According to analysts at cyber intelligence firm Flashpoint, between January and the end of March 2021, Babuk continued to post databases stolen from companies that refused to pay a ransom, but they posted the leaks to both their victim shaming blog and to multiple cybercrime forums, an unusual approach.
This matches the ethos and activity of Wazawaka’s posts on the crime forums over the past two years. As I wrote in January:
“Wazawaka seems to have adopted the uniquely communitarian view that when organizations being held for ransom decline to cooperate or pay up, any data stolen from the victim should be published on the Russian cybercrime forums for all to plunder — not privately sold to the highest bidder. In thread after thread on the crime forum XSS, Wazawaka’s alias ‘Uhodiransomwar’ can be seen posting download links to databases from companies that have refused to negotiate after five days.”
Around Apr. 27, 2021, Babuk hacked the Washington Metropolitan Police Department, demanding $4 million in virtual currency in exchange for a promise not to publish the police department’s internal data.
Flashpoint says that on April 30, Babuk announced they were shuttering the affiliate program and its encryption services, and that they would now focus on data theft and extortion instead. On May 3, the group posted two additional victims of their data theft enterprise, showing they are still in operation.
On May 11, 2021, Babuk declared negotiations with the MPD had reached an impasse, and leaked 250 gigabytes worth of MPD data.
On May 14, 2021, Boriselcin announced on XSS his intention to post a writeup on how they hacked the DC Police (Boriselcin claims it was via the organization’s VPN).
On May 17, Babuk posted about an upcoming new ransomware leaks site that will serve as a “huge platform for independent leaks,” — i.e., a community that would publish data stolen by no-name ransomware groups that don’t already have their own leaks/victim shaming platforms.
On May 31, 2021, Babuk’s website began redirecting to Payload[.]bin. On June 23, 2021, Biba99 posted to RaidForums saying he’s willing to buy zero-day vulnerabilities in corporate VPN products. Biba99 posts his unique user ID for Tox, a peer-to-peer instant messaging service.
On July 13, 2021, Payload[.]bin was renamed to RAMP, which according to Orange stands for “Ransom Anon Market Place.” Flashpoint says RAMP was created “directly in response to several large Dark Web forums banning ransomware collectives on their site following the Colonial Pipeline attack by ransomware group ‘DarkSide.” [links added]
“Babuk noted that this new platform will not have rules or ‘bosses,'” Flashpoint observed in a report on the group. “This reaction distinguishes Babuk from other ransomware collectives, many of which changed their rules following the attack to attract less attention from law enforcement.”
The RAMP forum opening was announced by the user “TetyaSluha. That nickname soon switched to “Orange,” who appears to have registered on RAMP with the email address “teresacox19963@gmail.com.” Recall that this is the same email address used by the spokesperson for the Babuk ransomware gang — Boriselcin/Biba99.
In a post on RAMP Aug. 18, 2021, in which Orange is attempting to recruit penetration testers, he claimed the same Tox ID that Biba99 used on RaidForums.
On Aug. 22, Orange announced a new ransomware affiliate program called “Groove,” which claimed to be an aggressive, financially motivated criminal organization dealing in industrial espionage for the previous two years.
In November 2021, Groove’s blog disappeared, and Boriselcin posted a long article to the XSS crime forum explaining that Groove was little more than a pet project to mess with the media and security industries.
On Sept. 13, 2021, Boriselcin posted to XSS saying he would pay handsomely for a reliable, working exploit for CVE-2021-20028, the same exploit that @fuck_maze would later release to Twitter on Jan. 25, 2022.
Asked for comment on this research, cyber intelligence firm Intel 471 confirmed that its analysts reached the same conclusion.
“We identified the user as the Russian national Михаил Павлович Матвеев aka Mikhail Pavlovich Matveev, who was widely known in the underground community as the actor using the Wazawaka handle, a.k.a. Alfredpetr, andry1976, arestedByFbi, boriselcin, donaldo, ebanatv2, futurama, gotowork, m0sad, m1x, Ment0s, ment0s, Ment0s, Mixalen, mrbotnet, Orange, posholnarabotu, popalvprosak, TetyaSluha, uhodiransomwar, and 999,” Intel 471 wrote.
As usual, I put together a rough mind map on how all these data points indicate a connection between Wazawaka, Orange, and Boriselcin.
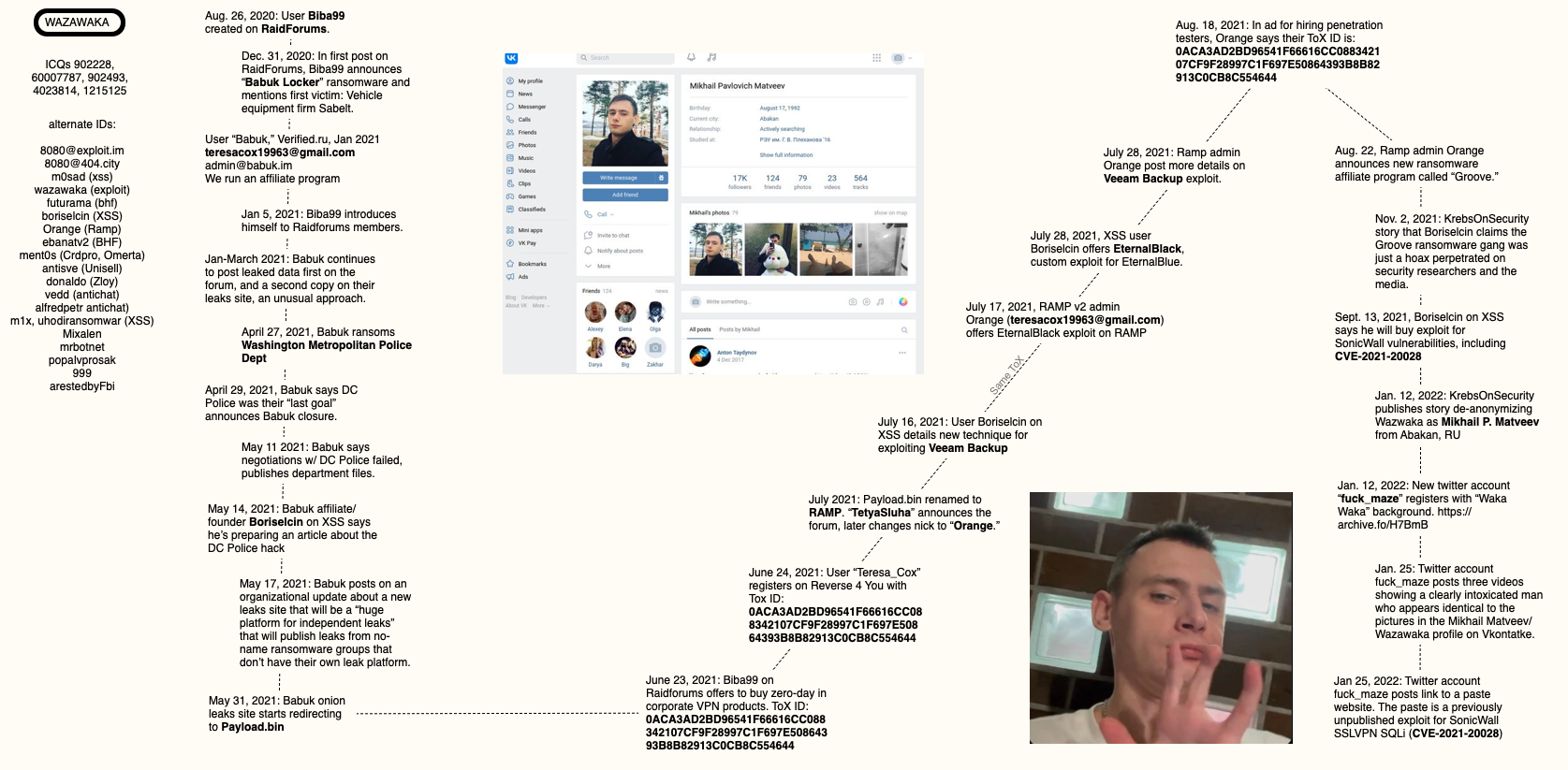
A mind map connecting Wazawaka to the RAMP forum administrator “Orange” and the founder of the Babuk ransomware gang.
As noted in January’s profile, Wazawaka has worked with at least two different ransomware affiliate programs, including LockBit. Wazawaka said LockBit had paid him roughly $500,000 in commissions for the six months leading up to September 2020.
Wazawaka also said he’d teamed up with DarkSide, the ransomware affiliate group responsible for the six-day outage at Colonial Pipeline last year that caused nationwide fuel shortages and price spikes. The U.S. Department of State has since offered a $5 million reward for information leading to the arrest and conviction of any DarkSide affiliates.






