Bloomberg published a story this week citing three unnamed sources who told the publication that Equifax experienced a breach earlier this year which predated the intrusion that the big-three credit bureau announced on Sept. 7. To be clear, this earlier breach at Equifax is not a new finding and has been a matter of public record for months. Furthermore, it was first reported on this Web site in May 2017.
 In my initial Sept. 7 story about the Equifax breach affecting more than 140 million Americans, I noted that this was hardly the first time Equifax or another major credit bureau has experienced a breach impacting a significant number of Americans.
In my initial Sept. 7 story about the Equifax breach affecting more than 140 million Americans, I noted that this was hardly the first time Equifax or another major credit bureau has experienced a breach impacting a significant number of Americans.
On May 17, KrebsOnSecurity reported that fraudsters exploited lax security at Equifax’s TALX payroll division, which provides online payroll, HR and tax services.
That story was about how Equifax’s TALX division let customers who use the firm’s payroll management services authenticate to the service with little more than a 4-digit personal identification number (PIN).
Identity thieves who specialize in perpetrating tax refund fraud figured out that they could reset the PINs of payroll managers at various companies just by answering some multiple-guess questions — known as “knowledge-based authentication” or KBA questions — such as previous addresses and dates that past home or car loans were granted.
On Tuesday, Sept. 18, Bloomberg ran a piece with reporting from no fewer than five journalists there who relied on information provided by three anonymous sources. Those sources reportedly spoke in broad terms about an earlier breach at Equifax, and told the publication that these two incidents were thought to have been perpetrated by the same group of hackers.
The Bloomberg story did not name TALX. Only post-publication did Bloomberg reporters update the piece to include a statement from Equifax saying the breach was unrelated to the hack announced on Sept. 7, and that it had to do with a security incident involving a payroll-related service during the 2016 tax year.
I have thus far seen zero evidence that these two incidents are related. Equifax has said the unauthorized access to customers’ employee tax records (we’ll call this “the March breach” from here on) happened between April 17, 2016 and March 29, 2017.
The criminals responsible for unauthorized activity in the March breach were participating in an insidious but common form of cybercrime known as tax refund fraud, which involves filing phony tax refund requests with the IRS and state tax authorities using the personal information from identity theft victims.
My original report on the March breach was based on public breach disclosures that Equifax was required by law to file with several state attorneys general.
Because the TALX incident exposed the tax and payroll records of its customers’ employees, the victim customers were in turn required to notify their employees as well. That story referenced public breach disclosures from five companies that used TALX, including defense contractor giant Northrop Grumman; staffing firm Allegis Group; Saint-Gobain Corp.; Erickson Living; and the University of Louisville.
When asked Tuesday about previous media coverage of the March breach, Equifax pointed National Public Radio (NPR) to coverage in KrebsonSecurity.
One more thing before I move on to the analysis. For more information on why KBA is a woefully ineffective method of stopping fraudsters, see this story from 2013 about how some of the biggest vendors of these KBA questions were all hacked by criminals running an identity theft service online.
Or, check out these stories about how tax refund fraudsters used weak KBA questions to steal personal data on hundreds of thousands of taxpayers directly from the Internal Revenue Service‘s own Web site. It’s probably worth mentioning that Equifax provided those KBA questions as well.
ANALYSIS
Over the past two weeks, KrebsOnSecurity has received an unusually large number of inquiries from reporters at major publications who were seeking background interviews so that they could get up to speed on Equifax’s spotty security history (sadly, Bloomberg was not among them).
These informational interviews — in which I agree to provide context and am asked to speak mainly on background — are not unusual; I sometimes field two or three of these requests a month, and very often more when time permits. And for the most part I am always happy to help fellow journalists make sure they get the facts straight before publishing them.
But I do find it slightly disturbing that there appear to be so many reporters on the tech and security beats who apparently lack basic knowledge about what these companies do and their roles in perpetuating — not fighting — identity theft.
It seems to me that some of the world’s most influential publications have for too long given Equifax and the rest of the credit reporting industry a free pass — perhaps because of the complexities involved in succinctly explaining the issues to consumers. Indeed, I would argue the mainstream media has largely failed to hold these companies’ feet to the fire over a pattern of lax security and a complete disregard for securing the very sensitive consumer data that drives their core businesses.
To be sure, Equifax has dug themselves into a giant public relations hole, and they just keep right on digging. On Sept. 8, I published a story equating Equifax’s breach response to a dumpster fire, noting that it could hardly have been more haphazard and ill-conceived.
But I couldn’t have been more wrong. Since then, Equifax’s response to this incident has been even more astonishingly poor.
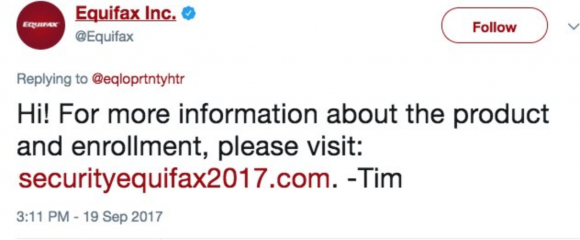
EQUIPHISH
On Tuesday, the official Equifax account on Twitter replied to a tweet requesting the Web address of the site that the company set up to give away its free one-year of credit monitoring service. That site is https://www.equifaxsecurity2017.com, but the company’s Twitter account told users to instead visit securityequifax2017[dot]com, which is currently blocked by multiple browsers as a phishing site.
FREEZING UP
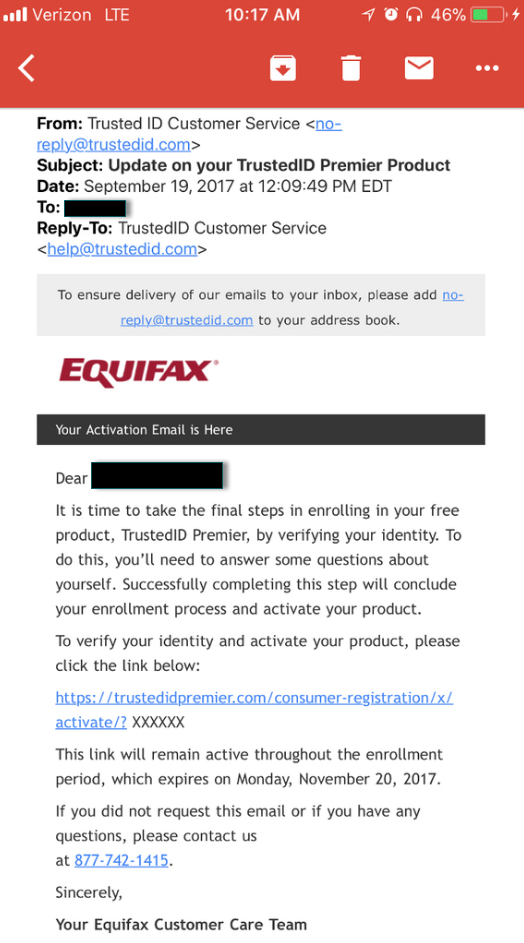
Under intense public pressure from federal lawmakers and regulators, Equifax said that for 30 days it would waive the fee it charges for placing a security freeze on one’s credit file (for more on what a security freeze entails and why you and your family should be freezing their files, please see The Equifax Breach: What You Should Know).
Unfortunately, the free freeze offer from Equifax doesn’t mean much if consumers can’t actually request one via the company’s freeze page; I have lost count of how many comments have been left here by readers over the past week complaining of being unable to load the site, let alone successfully obtain a freeze. Instead, consumers have been told to submit the requests and freeze fees in writing and to include copies of identity documents to validate the requests.
Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass) recently introduced a measure that would force the bureaus to eliminate the freeze fees and to streamline the entire process. To my mind, that bill could not get passed soon enough.
Understand that each credit bureau has a legal right to charge up to $20 in some states to freeze a credit file, and in many states they are allowed to charge additional fees if consumers later wish to lift or temporarily thaw a freeze. This is especially rich given that credit bureaus earn roughly $1 every time a potential creditor (or identity thief) inquires about your creditworthiness, according to Avivah Litan, a fraud analyst with Gartner Inc.
In light of this, it’s difficult to view these freeze fees as anything other than a bid to discourage consumers from filing them.
The Web sites where consumers can go to file freezes at the other major bureaus — including TransUnion and Experian — have hardly fared any better since Equifax announced the breach on Sept. 7. Currently, if you attempt to freeze your credit file at TransUnion, the company’s site is relentless in trying to steer you away from a freeze and toward the company’s free “credit lock” service.
That service, called TrueIdentity, claims to allow consumers to lock or unlock their credit files for free as often as they like with the touch of a button. But readers who take the bait probably won’t notice or read the terms of service for TrueIdentity, which has the consumer agree to a class action waiver, a mandatory arbitration clause, and something called ‘targeted marketing’ from TransUnion and their myriad partners.
The agreement also states TransUnion may share the data with other companies:
“If you indicated to us when you registered, placed an order or updated your account that you were interested in receiving information about products and services provided by TransUnion Interactive and its marketing partners, or if you opted for the free membership option, your name and email address may be shared with a third party in order to present these offers to you. These entities are only allowed to use shared information for the intended purpose only and will be monitored in accordance with our security and confidentiality policies. In the event you indicate that you want to receive offers from TransUnion Interactive and its marketing partners, your information may be used to serve relevant ads to you when you visit the site and to send you targeted offers. For the avoidance of doubt, you understand that in order to receive the free membership, you must agree to receive targeted offers.“
TransUnion then encourages consumers who are persuaded to use the “free” service to subscribe to “premium” services for a monthly fee with a perpetual auto-renewal.
In short, TransUnion’s credit lock service (and a similarly named service from Experian) doesn’t prevent potential creditors from accessing your files, and these dubious services allow the credit bureaus to keep selling your credit history to lenders (or identity thieves) as they see fit.
As I wrote in a Sept. 11 Q&A about the Equifax breach, I take strong exception to the credit bureaus’ increasing use of the term “credit lock” to divert people away from freezes. Their motives for saddling consumers with even more confusing terminology are suspect, and I would not count on a credit lock to take the place of a credit freeze, regardless of what these companies claim (consider the source).
Experian’s freeze Web site has performed little better since Sept. 7. Several readers pinged KrebsOnSecurity via email and Twitter to complain that while Experian’s freeze site repeatedly returned error messages stating that the freeze did not go through, these readers’ credit cards were nonetheless charged $15 freeze fees multiple times.
If the above facts are not enough to make your blood boil, consider that Equifax and other bureaus have been lobbying lawmakers in Congress to pass legislation that would dramatically limit the ability of consumers to sue credit bureaus for sloppy security, and cap damages in related class action lawsuits to $500,000.
If ever there was an industry that deserved obsolescence or at least more regulation, it is the credit bureaus. If either of those outcomes are to become reality, it is going to take much more attentive and relentless coverage on the part of the world’s top news publications. That’s because there’s a lot at stake here for an industry that lobbies heavily (and successfully) against any new laws that may restrict their businesses.
Here’s hoping the media can get up to speed quickly on this vitally important topic, and help lead the debate over legal and regulatory changes that are sorely needed.
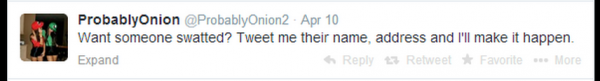
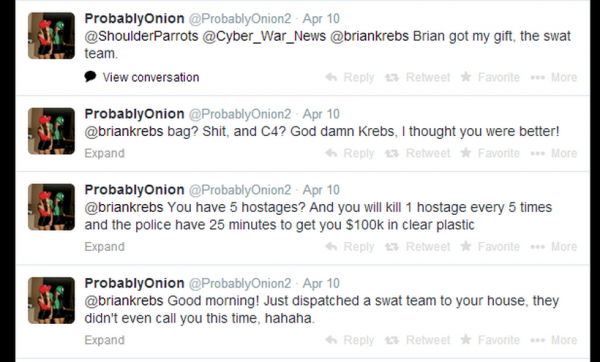
 In
In 
