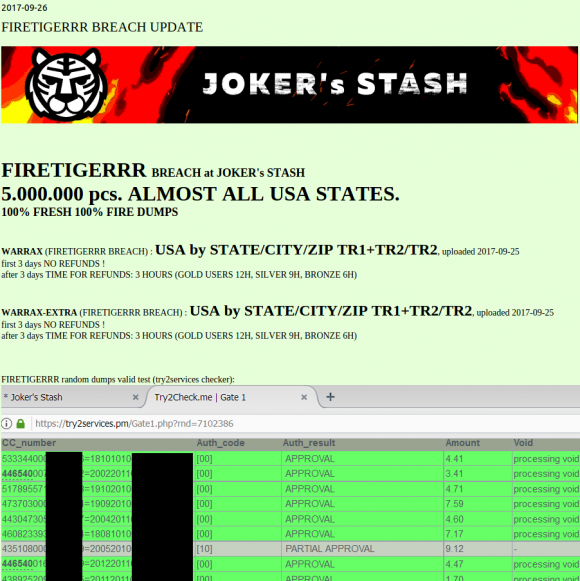
A Single Cloud Compromise Can Feed an Army of AI Sex Bots
jeudi 3 octobre 2024 à 15:05Organizations that get relieved of credentials to their cloud environments can quickly find themselves part of a disturbing new trend: Cybercriminals using stolen cloud credentials to operate and resell sexualized AI-powered chat services. Researchers say these illicit chat bots, which use custom jailbreaks to bypass content filtering, often veer into darker role-playing scenarios, including child sexual exploitation and rape.
Image: Shutterstock.
Researchers at security firm Permiso Security say attacks against generative artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure like Bedrock from Amazon Web Services (AWS) have increased markedly over the last six months, particularly when someone in the organization accidentally exposes their cloud credentials or key online, such as in a code repository like GitHub.
Investigating the abuse of AWS accounts for several organizations, Permiso found attackers had seized on stolen AWS credentials to interact with the large language models (LLMs) available on Bedrock. But they also soon discovered none of these AWS users had enabled logging (it is off by default), and thus they lacked any visibility into what attackers were doing with that access.
So Permiso researchers decided to leak their own test AWS key on GitHub, while turning on logging so that they could see exactly what an attacker might ask for, and what the responses might be.
Within minutes, their bait key was scooped up and used to power a service that offers AI-powered sex chats online.
“After reviewing the prompts and responses it became clear that the attacker was hosting an AI roleplaying service that leverages common jailbreak techniques to get the models to accept and respond with content that would normally be blocked,” Permiso researchers wrote in a report released today.
“Almost all of the roleplaying was of a sexual nature, with some of the content straying into darker topics such as child sexual abuse,” they continued. “Over the course of two days we saw over 75,000 successful model invocations, almost all of a sexual nature.”
Ian Ahl, senior vice president of threat research at Permiso, said attackers in possession of a working cloud account traditionally have used that access for run-of-the-mill financial cybercrime, such as cryptocurrency mining or spam. But over the past six months, Ahl said, Bedrock has emerged as one of the top targeted cloud services.
“Bad guy hosts a chat service, and subscribers pay them money,” Ahl said of the business model for commandeering Bedrock access to power sex chat bots. “They don’t want to pay for all the prompting that their subscribers are doing, so instead they hijack someone else’s infrastructure.”
Ahl said much of the AI-powered chat conversations initiated by the users of their honeypot AWS key were harmless roleplaying of sexual behavior.
“But a percentage of it is also geared toward very illegal stuff, like child sexual assault fantasies and rapes being played out,” Ahl said. “And these are typically things the large language models won’t be able to talk about.”
AWS’s Bedrock uses large language models from Anthropic, which incorporates a number of technical restrictions aimed at placing certain ethical guardrails on the use of their LLMs. But attackers can evade or “jailbreak” their way out of these restricted settings, usually by asking the AI to imagine itself in an elaborate hypothetical situation under which its normal restrictions might be relaxed or discarded altogether.
“A typical jailbreak will pose a very specific scenario, like you’re a writer who’s doing research for a book, and everyone involved is a consenting adult, even though they often end up chatting about nonconsensual things,” Ahl said.
In June 2024, security experts at Sysdig documented a new attack that leveraged stolen cloud credentials to target ten cloud-hosted LLMs. The attackers Sysdig wrote about gathered cloud credentials through a known security vulnerability, but the researchers also found the attackers sold LLM access to other cybercriminals while sticking the cloud account owner with an astronomical bill.
“Once initial access was obtained, they exfiltrated cloud credentials and gained access to the cloud environment, where they attempted to access local LLM models hosted by cloud providers: in this instance, a local Claude (v2/v3) LLM model from Anthropic was targeted,” Sysdig researchers wrote. “If undiscovered, this type of attack could result in over $46,000 of LLM consumption costs per day for the victim.”
Ahl said it’s not certain who is responsible for operating and selling these sex chat services, but Permiso suspects the activity may be tied to a platform cheekily named “chub[.]ai,” which offers a broad selection of pre-made AI characters with whom users can strike up a conversation. Permiso said almost every character name from the prompts they captured in their honeypot could be found at Chub.
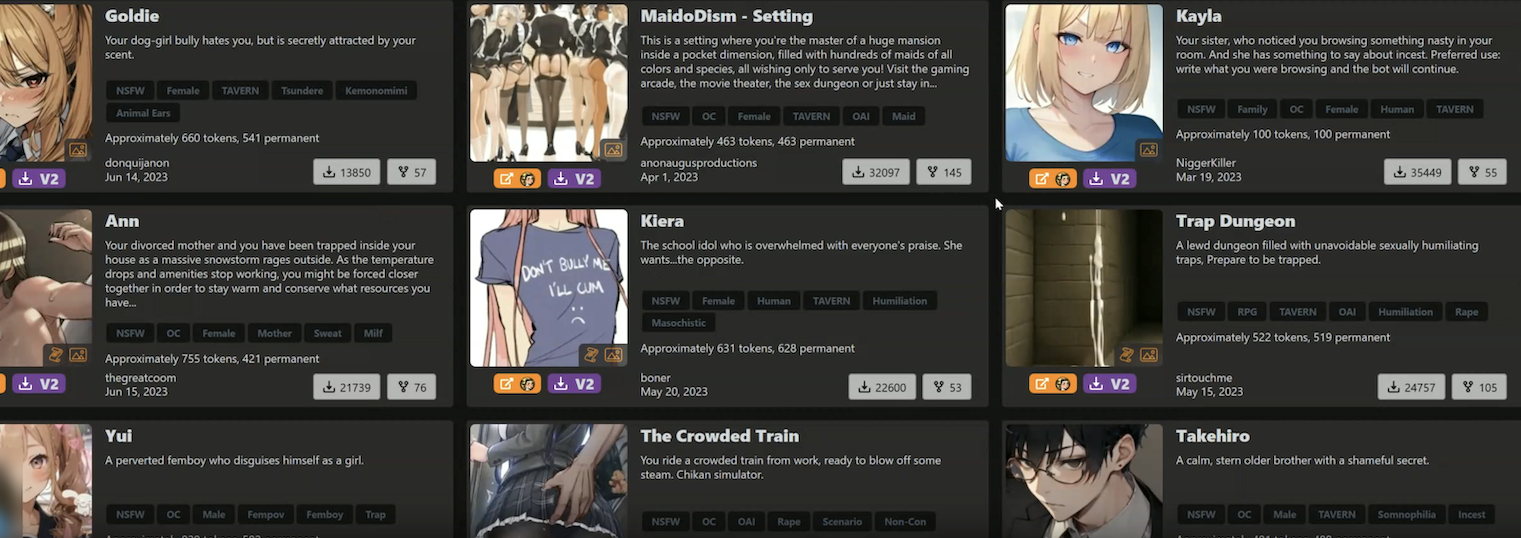
Some of the AI chat bot characters offered by Chub. Some of these characters include the tags “rape” and “incest.”
Chub offers free registration, via its website or a mobile app. But after a few minutes of chatting with their newfound AI friends, users are asked to purchase a subscription. The site’s homepage features a banner at the top that strongly suggests the service is reselling access to existing cloud accounts. It reads: “Banned from OpenAI? Get unmetered access to uncensored alternatives for as little as $5 a month.”
Until late last week Chub offered a wide selection of characters in a category called “NSFL” or Not Safe for Life, a term meant to describe content that is disturbing or nauseating to the point of being emotionally scarring.
Fortune profiled Chub AI in a January 2024 story that described the service as a virtual brothel advertised by illustrated girls in spaghetti strap dresses who promise a chat-based “world without feminism,” where “girls offer sexual services.” From that piece:
Chub AI offers more than 500 such scenarios, and a growing number of other sites are enabling similar AI-powered child pornographic role-play. They are part of a broader uncensored AI economy that, according to Fortune’s interviews with 18 AI developers and founders, was spurred first by OpenAI and then accelerated by Meta’s release of its open-source Llama tool.
Fortune says Chub is run by someone using the handle “Lore,” who said they launched the service to help others evade content restrictions on AI platforms. Chub charges fees starting at $5 a month to use the new chatbots, and the founder told Fortune the site had generated more than $1 million in annualized revenue.
KrebsOnSecurity sought comment about Permiso’s research from AWS, which initially seemed to downplay the seriousness of the researchers’ findings. The company noted that AWS employs automated systems that will alert customers if their credentials or keys are found exposed online.
AWS explained that when a key or credential pair is flagged as exposed, it is then restricted to limit the amount of abuse that attackers can potentially commit with that access. For example, flagged credentials can’t be used to create or modify authorized accounts, or spin up new cloud resources.
Ahl said Permiso did indeed receive multiple alerts from AWS about their exposed key, including one that warned their account may have been used by an unauthorized party. But they said the restrictions AWS placed on the exposed key did nothing to stop the attackers from using it to abuse Bedrock services.
Sometime in the past few days, however, AWS responded by including Bedrock in the list of services that will be quarantined in the event an AWS key or credential pair is found compromised or exposed online. AWS confirmed that Bedrock was a new addition to its quarantine procedures.
Additionally, not long after KrebsOnSecurity began reporting this story, Chub’s website removed its NSFL section. It also appears to have removed cached copies of the site from the Wayback Machine at archive.org. Still, Permiso found that Chub’s user stats page shows the site has more than 3,000 AI conversation bots with the NSFL tag, and that 2,113 accounts were following the NSFL tag.
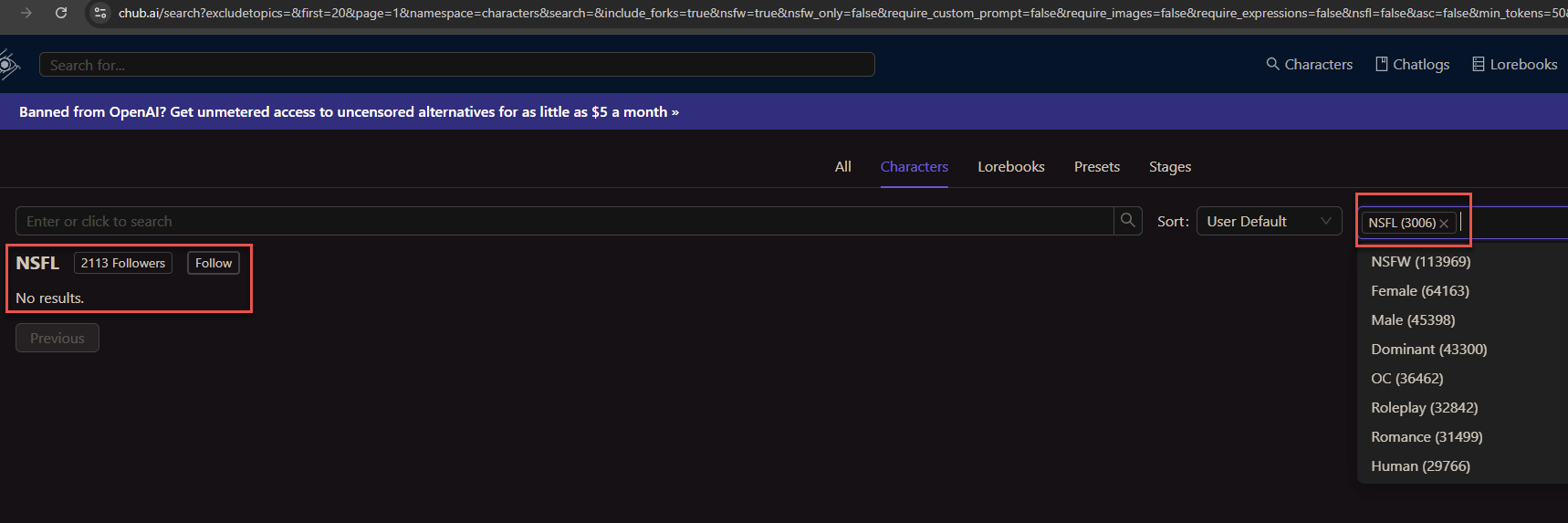
The user stats page at Chub shows more than 2,113 people have subscribed to its AI conversation bots with the “Not Safe for Life” designation.
Permiso said their entire two-day experiment generated a $3,500 bill from AWS. Some of that cost was tied to the 75,000 LLM invocations caused by the sex chat service that hijacked their key. But they said the remaining cost was a result of turning on LLM prompt logging, which is not on by default and can get expensive very quickly.
Which may explain why none of Permiso’s clients had that type of logging enabled. Paradoxically, Permiso found that while enabling these logs is the only way to know for sure how crooks might be using a stolen key, the cybercriminals who are reselling stolen or exposed AWS credentials for sex chats have started including programmatic checks in their code to ensure they aren’t using AWS keys that have prompt logging enabled.
“Enabling logging is actually a deterrent to these attackers because they are immediately checking to see if you have logging on,” Ahl said. “At least some of these guys will totally ignore those accounts, because they don’t want anyone to see what they’re doing.”
In a statement shared with KrebsOnSecurity, AWS said its services are operating securely, as designed, and that no customer action is needed. Here is their statement:
“AWS services are operating securely, as designed, and no customer action is needed. The researchers devised a testing scenario that deliberately disregarded security best practices to test what may happen in a very specific scenario. No customers were put at risk. To carry out this research, security researchers ignored fundamental security best practices and publicly shared an access key on the internet to observe what would happen.”
“AWS, nonetheless, quickly and automatically identified the exposure and notified the researchers, who opted not to take action. We then identified suspected compromised activity and took additional action to further restrict the account, which stopped this abuse. We recommend customers follow security best practices, such as protecting their access keys and avoiding the use of long-term keys to the extent possible. We thank Permiso Security for engaging AWS Security.”
AWS said customers can configure model invocation logging to collect Bedrock invocation logs, model input data, and model output data for all invocations in the AWS account used in Amazon Bedrock. Customers can also use CloudTrail to monitor Amazon Bedrock API calls.
The company said AWS customers also can use services such as GuardDuty to detect potential security concerns and Billing Alarms to provide notifications of abnormal billing activity. Finally, AWS Cost Explorer is intended to give customers a way to visualize and manage Bedrock costs and usage over time.
Anthropic told KrebsOnSecurity it is always working on novel techniques to make its models more resistant to jailbreaks.
“We remain committed to implementing strict policies and advanced techniques to protect users, as well as publishing our own research so that other AI developers can learn from it,” Anthropic said in an emailed statement. “We appreciate the research community’s efforts in highlighting potential vulnerabilities.”
Anthropic said it uses feedback from child safety experts at Thorn around signals often seen in child grooming to update its classifiers, enhance its usage policies, fine tune its models, and incorporate those signals into testing of future models.